1
Steph W. from SEOPressor


👋 Hey there! Would you like to try out this New AI-Powered App that'll...
...help you check your website and tell you exactly how to rank higher?

68
score %
SEO Score

Found us from search engine?
We rank high, you can too.
SEOPressor helps you to optimize your on-page SEO for higher & improved search ranking.
By winniewong on September 18, 2015
In late February of 2015, screams could be heard from half the marketing offices in the nation – Google had announced an algorithm change dubbed “Mobilegeddon” that was going to drastically affect mobile search results. Given that many other algorithm changes were simply implemented without notice, the fact that this time around website owners are given two months of warning was an indicator of just how big this change was going to be.
However, that’s not to say that every office was panicking – the most capable marketing teams already knew this was coming because they’d kept up-to-date with Google’s patents and could reliably predict what changes were coming next. If you really want to stay ahead of the game, this is the information you should be looking at – and here, we’ll show you how it works with three of Google’s larger updates and the patents that let us predict them.

This update to the Google algorithm focused on the idea that content should be fresh and relevant – especially if it was related to news or other time-sensitive topics. This particular update had three major patents associated with it, each one focused on an important subset of the overall update.
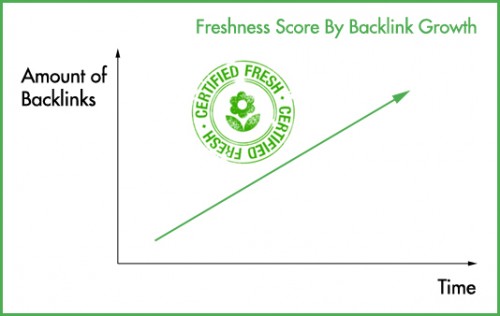
An increasing amount of backlink is a signal of Fresh contents while a dwindling amount is the sign of a content becoming stale.
Originally filed in January, this patent focused on the idea that measuring backlinks over time was a good way to help measure how “fresh” a given piece of content was. Essentially, the Google algorithm started to reward getting backlinks over a period of time, rather than all at once.
It also focused on comparing how many backlinks a website was getting. On average, a site that gets a similar number of backlinks on a regular basis is considered fresh, while having it dwindle over time suggests the page is no longer as relevant as it may have been in the past.

Links from other Fresh sources will increase your Freshness score as well.
The Google algorithm uses many ways of determining how fresh a document is – that’s what the Freshness Update was all about – but this patent was filed almost a year before it was fully implemented and served as an excellent early warning sign that something was going to happen.
At its core, this patent focused on the idea that being linked to by fresh content was better than being linked to by stale content. Of course, it’s hard to control a link once it’s earned, and getting a lot of links from sites that don’t update themselves could actually drag your own website down.
The solution is something you were probably doing anyway – focus on obtaining links from high-quality, regularly-updated sites (you know, the kind people are actually visiting).
Sometimes, the patents appear literally days before a big update goes live. That was the case with this patent, which focused on the idea that a search result that attracts user actions (clicking, reading, bookmarking or downloading files) are fresher than search results that receive fewer attention from the user.

A search result will be considered Fresh if they receive increased user activity.
It’s easy to see why Google does this. Say among the ten results in Google’s first page, suddenly result #7 receives an influx of user activity. A recent event must’ve triggered this as users suddenly finds this particular result interesting while other results remains pretty much the same. This might trigger Google to apply Freshness scoring to that particular search query and bump result #7 to the top of the page.
In this case, the page titles and meta description plays a huge role. If you notice your content is related to a trending event or topic, you can repurpose your content by updating its title and meta description to relate them closer to the trending subject. No matter how fantastic the contents are, if what little that is shown on Google search results page doesn’t reflect the query intention, users might not even click it and that’s a waste of a good content.
Other than attracting visitors in, do ensure that they stay and engage to further increase the activity signal to Google.
The Results:
According to Google, this update affected about 35% of searches, and for the most part impacted time-sensitive results (like news pages). Content that’s not time-sensitive, perhaps unsurprisingly, wasn’t disturbed very much. At the same time, however, this did encourage people to start improving their efforts at earning links – and simultaneously discouraged spam attempts, such as generating a bunch of fake links to try and trick the system.

As the name implies, the Mobile Update was a change to the Google algorithm focused around access from mobile devices (smartphones, tablets, etc.). In the last few years, mobile searches have become a significant part of the overall searching people do, and Google wanted to encourage websites to follow through with content that can be displayed properly on mobile devices.
Now here’s a patent that might prevent a lot of people from panicking if they’ve seen it before Google actually implemented the infamous Mobile Friendly Update. It was published in late 2013 – almost 2 years before the implementation. This patent covered the differences between normal and mobile queries and how different algorithms will be used to generate results for each.
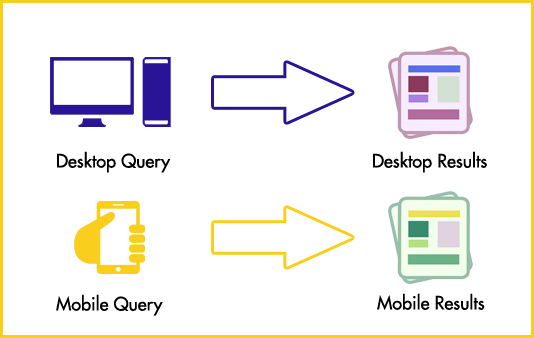
Mobile queries prioritizes mobile results and vice-versa.
In a nutshell, the patent mentions that mobile results will be prioritized to answer mobile queries and non-mobile results will be prioritized to answer generic desktop searches. For this reason, it’s actually okay not to optimize a website for mobile users if they aren’t your target group as it won’t affect the generic search.
Of course, considering that the amount of mobile queries are on the rise, it’s a good rule of thumb to make sure you optimize your website for both mobile and generic but it’s not really a pressing concern. Also according to the patent, Google will sometime prioritize websites that’s dedicated to their platform, meaning either purely designed for desktop and vice-versa instead of balanced ones.
So if your traffic heavily relies on just one platform, trying to go for both might actually be detrimental.
One of the most practiced way of making a website mobile friendly is to create a mobile version of it that’s simpler and less cluttered so that it can be displayed better on mobile devices. However, sometimes people oversimplify the mobile version of their websites that it’s missing certain factors that Google needed to use as ranking factors.

The good news is, this patent describes that in this case, an algorithm is implemented for Google to rank the mobile website with insufficient ranking data parallel to the ranking of its desktop version on generic search. But what we can also learn is, by oversimplifying a mobile version of a website, it can actually strip it off some important ranking data that is required by Google.
Although a workaround is put in place, we can tell that oversimplified websites are actually an issue for Google and the band-aid fix might not be as efficient or accurate at ranking compared to the algorithm employed in normal circumstances. Instead of taking the chance it’s a good idea to be careful not to oversimplify your mobile version of websites and help make it easier for Google to rank your site.
The Results:
Less disruption than expected, actually, leading some people to believe that the “Mobilegeddon” name was a bit overdone – except for those who’d been doing things poorly to start with and found all of their plans upset, anyway. On the other hand, had those people been looking at Google’s patents, they could have predicted this Google algorithm change as early as 2013 – paying attention really does help.

One of the most important things to come out of the spread of mobile search results is an emphasis on local searches. For example, if someone is using a mobile device and searching for “coffee shop”, they’re probably most interested in coffee shops close to their current location. In the same vein, if they search for “traffic” while on the move, they probably want to know about any traffic issues on the road they’re currently driving on.
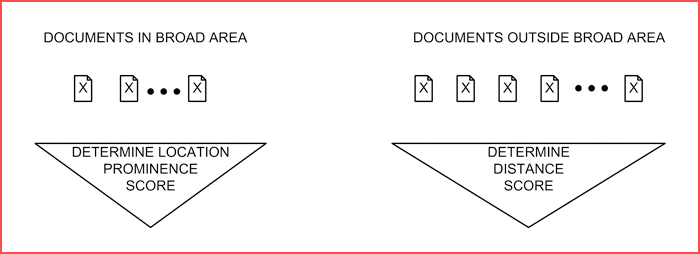
How Local Search Prominence is determined.
This patent was filed a few months before the Venice update went live, and strongly emphasized location-based information for local searches. A major part of this was the Local Search Prominence – an algorithm to rank local results differently than generic search. Local Search Prominence prioritizes results that’s nearest to the user.
Based on this patent, there are 2 ways of ranking local results:
The Results:
Moz notes that the exact rollout date of this update is unclear, but the 27th of February is when they believe it happened. The update also served to tightly integrate the Name, Address, and Phone Numbers of businesses, making consistency an important part of this Google algorithm update.
As you can see from the examples up above, watching patents can give you months of warning and let you continue your ascent to the top once things start changing. With that in mind, let’s look at some patents that have been filed but aren’t a main part of the algorithm quite yet – there’s no telling when updates containing them will go live, but you might want to consider adjusting your strategy now…

Mainly aimed at video contents, this patent describes a ranking system based on how long a content is watched by the user. While most probably will be used to rank results in Google video search, the system might also be used in other situations – perhaps as a factor to judge a website’s quality based on whether videos are used in the contents and if readers spend any time watching them.
Considering email marketing are widely used today to both promote the products as well as contents of a website, this could potentially be a big change in the future. Negative signals such as the tendency to get reported as spam or high unsubscribe rate might be used by Google to detrimentally affect a website’s ranking. On the bright side, maybe positive signals such as high click-through-rate and email forwarding can in turn help boost your ranking.
I can already imagine “Google Email Ranking Update” to be a huge topic if this is implemented and people will start talking about “email SEO”.
If you’ve used Google in the last few years, you may have noticed that they’re offering new kinds of content in the search results pages – for example, rather than giving links to web pages when people ask “When is Elvis’s birthday?”, it’s just going to flat-out tell you and maybe show some web pages with that information.
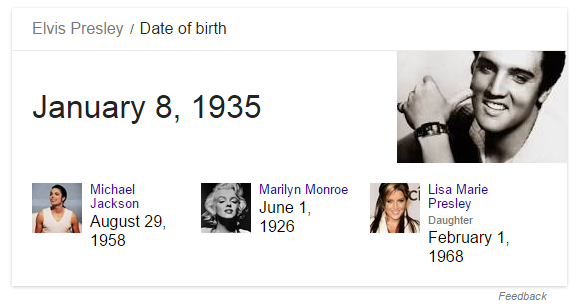
Rich answers might show up in more searches in the future.
Essentially, people using a search engine want answers, not just web pages. The way Google is achieving this is through its Knowledge Graph initiative. While currently estimated to cover roughly 25% of queries, this number most probably will grow and might even completely replace conventional search results eventually.
The way to help prepare your website for this case is by making it easier for Google to understand your website, contents and each of their components. Achieving this warrants a topic of its own but for starters, it’s a good idea to start using schema markup to label your website contents.

The idea here is that if Google knows what you’re watching, it can deliver more-personalized results. A common example is that if you’re currently viewing a cooking show and search for a certain type of food, the Google algorithm can understand what that food is and probably show you a recipe for it.
Although it sounds quite futuristic, the application for this patent might be sooner than you think considering that smart televisions connected to the net is starting to gain market share. A lot of people also watches tv on their other smart devices and it’s worth noticing that most of these are powered by Google’s Android OS.
This patent is all about driving and getting people to various places. In the past, driving directions have been ranked primarily on distance and travel time, with the default assumption being that shorter is better. This patent, however, is starting to take considerations like road smoothness into consideration, and you can expect it to be tightly integrated into driverless cars – after all, driving on smoother roads tends to reduce repair costs!
This algorithm might impact local SEO in the future. Like what I have mentioned in the Google Venice section, currently Google uses distance from user as a factor in ranking local search results. In the future, road quality might probably be included in the mix as well.
Patents are easily one of the best indicators of where Google is going with its search algorithm. When you pay attention to them, you’ll know what’s happening next – and when you can base your SEO plans around the future, you can hit the ground running and take advantage of every algorithm update. This is importan
Updated: 15 April 2024
Gotcha.

Generate 5,000 words in under 5 minutes

Publish 100+ blog posts monthly

Rank in the Top 10 with SEO-optimized content

Drive 500K organic traffic
Rank in the Top 10 now with Longform AI
Save 67% today (As low as $14.69/mo)
