Steph W. from SEOPressor


...help you check your website and tell you exactly how to rank higher?
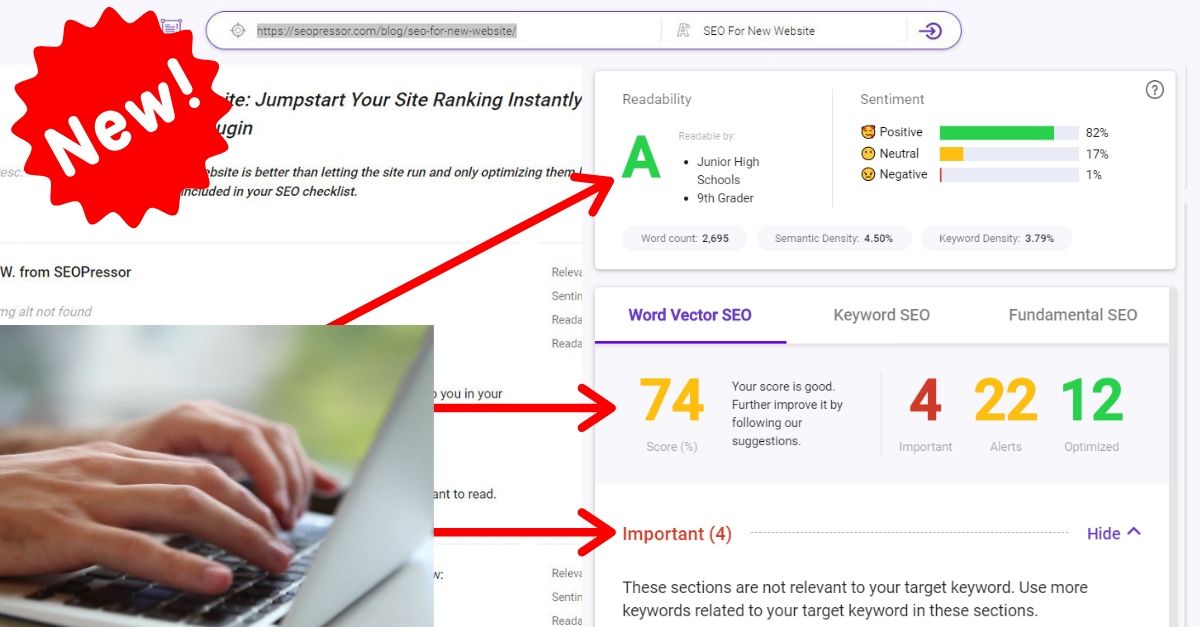

82
score %
SEO Score

Found us from search engine?
We rank high, you can too.
SEOPressor helps you to optimize your on-page SEO for higher & improved search ranking.
By vivian on January 13, 2016

There are a lot of things that make SEO and content marketing unlike any other form of marketing that’s come before, but perhaps biggest of all is that SEO is completely reliant on outside parties to succeed. With more than two-thirds of all global search traffic going through its systems, Google is more than a mere partner in advertising.
They basically call the shots.
Furthermore, Google sees themselves as serving the public interests, rather than those of private marketers. Google’s position as the proverbial 800-pound gorilla is largely based on there being hundreds of millions of people who voluntarily use their services every day, even when alternatives like Microsoft Bing exist.
Their focus is on serving up the best possible search results to the widest possible audience, and they do not hesitate to make changes to their search algorithms aimed at facilitating this.
In turn, this puts online marketers in a somewhat awkward situation. To keep their placement in Google’s search results high, it means constantly being aware of Google’s rules and regulations.
Failure to adhere to Google’s expectations can easily bring the dreaded Google Penalty: Automatic downgrades or even outright bans, based on behavior which Google sees as being against their principles of good search results.
One of the absolute requirements of successful SEO is avoiding Google Penalties. This paper will discuss what those penalties are, and how best to prevent them.
Broadly speaking, Google wants their search results to be organic. They want the best websites to naturally rise to the top of search pages, based on both quality of content and the number of users reading/linking to those pages.
Accordingly, they strongly resist attempts to “game” their system, using cheap tricks to artificially inflate the perceived popularity or relevance of a certain website.
As a group, these are called “black hat” techniques. We’ll discuss them in depth further down. But first, let’s look at the three major types of Google Penalty that may be imposed:
While rare, Google is willing to hand out a virtual “death penalty” to websites which flagrantly abuse the system or engage in truly unethical/illegal behavior such as distributing malware.
It’s very hard to accidentally get banned. A website has to be going over the top to get de-listed entirely, to the point that someone in the operation will be aware that they’re playing dangerous games.
Google is also willing to censor extremely violent, racist, or otherwise socially-unacceptable content, but this is also rare and something readers of this paper will almost certainly not be engaging in.
The most standard Google Penalty is rank demotion: A website goes suddenly from being highly-ranked to having a much lower rank, usually one that’s below the first page of results.
This can have the most possible causes as well, generally due to running afoul of algorithms looking to screen out “black hat” techniques.
Rank demotions can happen accidentally, but will still require direct action to fix. We’ll discuss this in the third part of this paper.
Beyond automated rank changes, Google also has an entire team who are empowered to manually de-rank webpages they believe are cheating in some way or another. The difference here is that often -not always- Google will directly notify the website of the problem and suggest ways of reversing the rank demotion.
Follow their suggestions, and your status will almost always be restored.
If your website is already a full part of the Google network, with a profile and Google Business listing and AdWords integration, the chances are far higher you’ll receive this direct notification. This is another reason that fully filling-out Google profiles for your business is a good idea.
It’s usually not hard to know if you’ve been penalized, so there isn’t that much to say here. A webmaster who keeps up with their site metrics will be able to spot one relatively quickly.
Here are the major warning signs:
Basically, any website that tracks its metrics on a daily or weekly basis won’t have a Google Penalty for too long without realizing it. Google isn’t trying to be sneaky and, whenever possible, they want webmasters to have a chance to fix their site and restore their ranking.
A Google Penalty isn’t handed out randomly, since Google wants as many quality websites present as possible. Most of the time, penalties come when a website is failing to comply with their Webmaster Guidelines, which is one of the most important pages online for an SEO marketer.
There is an ever-growing list of “tricks” which Google will automatically penalize a website for engaging in, if spotted. These include, but are not limited to:
This is a relatively new concern among webmasters, but one which (unfortunately) follows logically from Google’s focus on enforcing their rules. Negative SEO is a deliberate attempt on the part of one website to make a competitor look like they’re engaging in ‘black hat’ techniques.
If successful, this invokes a Google Penalty against the target.
It’s very dirty pool but it can also be hard to detect, which makes negative SEO attractive to unscrupulous businesses or even cyber-criminals looking to extort legitimate sites.
The most common form of negative SEO utilizes link farms, submitting your URL to those farms and then hoping Google notices and blames you for it.
They may also abuse copyright systems, submitting false claims of IP infringement in hopes of making you look shady. They could even go so far as to copy your content to their page, then falsify fileaccess dates to make it appear you ripped them off.
Occasionally, negative SEO can also involve direct hacking, although this is extremely rare. There are cases on record of hackers altering a site’s meta-text or robots.txt file to invoke a Google Penalty.
However, most of the time, if a hacker has enough access to your system to do this, they’re going to cause more overt damage instead. Good security practices will usually render this a non-issue.
The good news is that Google is very aware of negative SEO and will be sympathetic if you have evidence that it’s happening to you.
While most of the time a Google Penalty requires deliberate action, it’s possible to run afoul of their guidelines by accident. Much of the time, this is due to using outdated SEO techinques.
Keyword stuffing used to be far more common, for example, and even a successful technique. Likewise, many link aggregators that were previously acceptable are now seen as link farms instead.
If you find yourself suffering a Google Penalty without knowing why, usually the best course of action is to just ask. Google will work with webmasters who reach out for guidance.
Finally, we just wanted to mention that nothing here should be taken to indicate an adversarial relationship between Google and advertisers. Google is fully aware that marketers rely on them for exposure. They are consistently up-front with their own company goals and expectations from websites who rely on their search engine for placement.
The best way to avoid penalties is simply to pay attention to Google’s announcements regarding changes to their search engine, and maintain compliance with their webmaster guidelines.
That’s it for this discussion. Stay tuned for our next major Google-focused paper, which will focus on recovering from Google Penalties once they’ve appeared and solidifying your search engine placement.
Updated: 4 March 2026

Save thousands of dollars (it’s 100x cheaper)

Zero risk of Google penalty (it’s Google-approved)

Boost your rankings (proven by case studies)
Rank High With This Link Strategy
Precise, Simplified, Fast Internal Linking.
