Steph W. from SEOPressor


...help you check your website and tell you exactly how to rank higher?
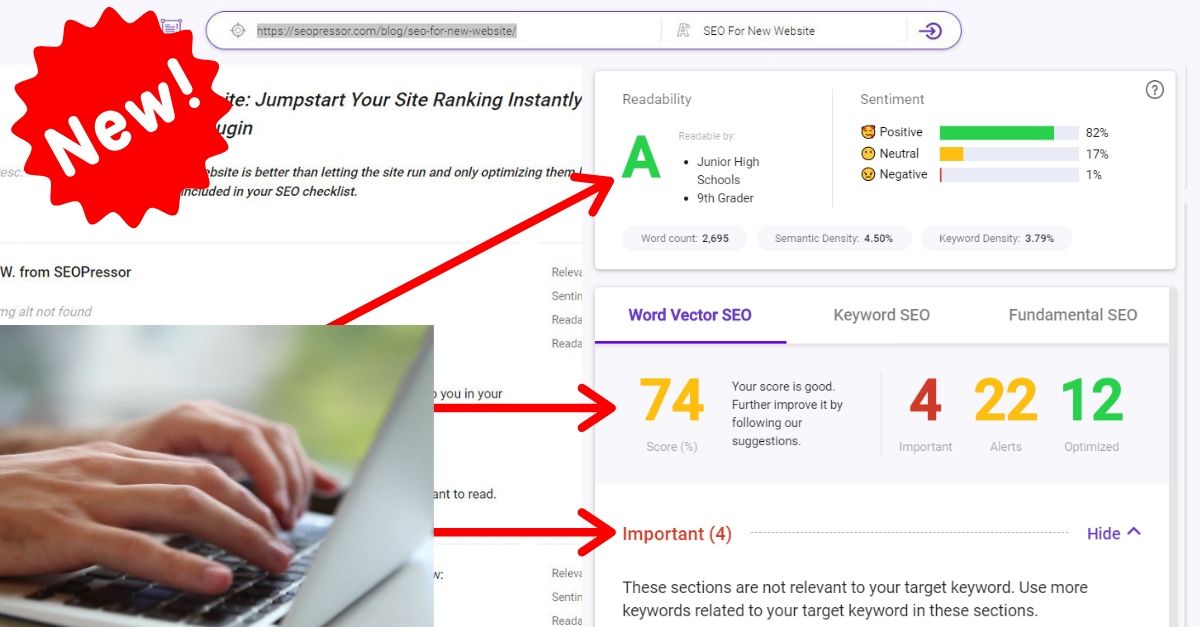

80
score %
SEO Score

Found us from search engine?
We rank high, you can too.
SEOPressor helps you to optimize your on-page SEO for higher & improved search ranking.
By vivian on July 31, 2019

Ever typed in an URL or clicked on an URL but when you land on the page, you noticed that the URL has changed?

That’s weird…
You’re not the only one who has experienced this. Once in a while, we do come across changes of website URL. So, why did the URL change by itself?
The answer is simple; we have been redirected to another webpage. So… what do I mean when I say we’ve been “redirected”? Search Engine Journal explains it in a perfectly simple way.
“A redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a different URL from the one they originally requested.”
Do take note that a redirect does not necessarily point to a website of the same domain only. A redirect can bring users to another domain as well.
Redirect is one of the five classes of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. URL Redirect is also known as URL Forwarding. The status codes are issued as a result of the request made by a client to the server. The five classes are as below:
This category is divided into nine HTTP status code, ranging from 300 to 308. The status code category signifies that additional action must be taken to complete a request.
I’ll let Wikipedia do the explanation of the 9 HTTP status code this time. Click on the image below to enlarge.
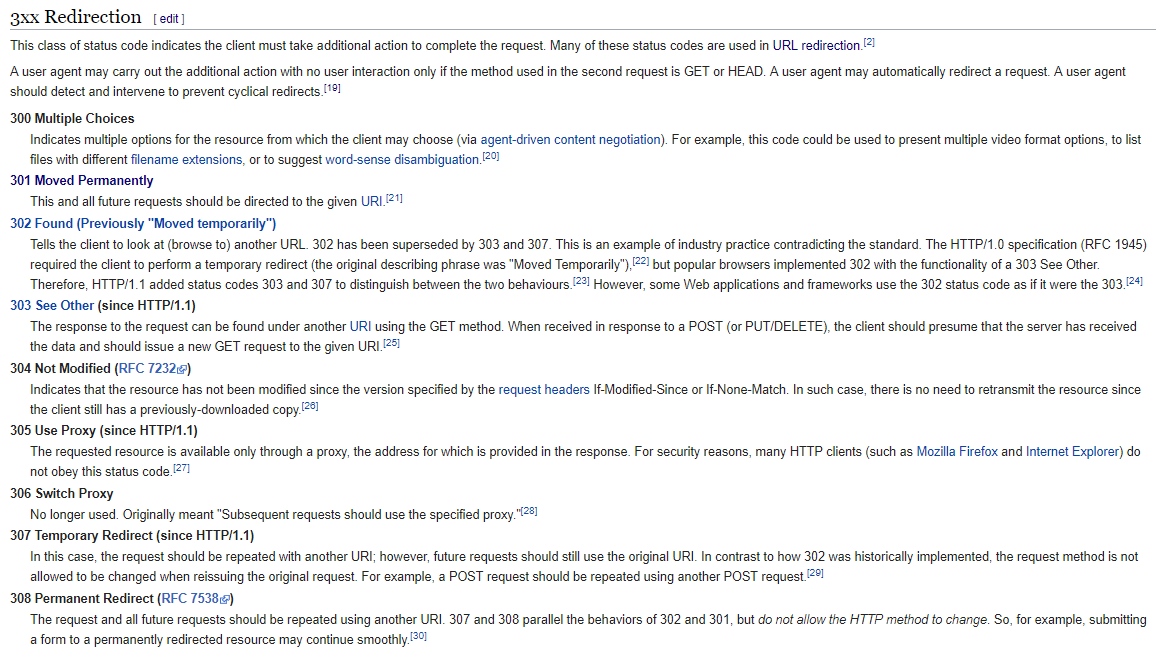
Source: Wikipedia
Out of the 9 HTTP status code, 301 and 302 are the ones we experience most often. Hence, I will focus on them in this article.
The two redirects are both server-side redirects. It occurs when there is a request made to the webserver and the webserver replies with a status code, which lets the client know that the documents they’ve requested have moved to another place.

A 301 Redirect is known as “Moved Permanently”. 301 Redirects tells Google that the webpage has permanently shifted to another webpage.
For instance, if you think that the domain name you’ve created 2 years ago needs a change for good, perhaps to a shorter and a more relevant name, you use a 301 redirect.
Google will then transfer link juice from your old site to your new site.
Here’s how you can think of the 301 redirect:
You sold off your house (old website) and bought a new one (new website). You then need to inform the postal service (search engine) to send mails (traffic) to your new address.
Or even better… Experience it yourself here! Try doing a navigational search. Type in SEOmoz.com and watch yourself land on Moz.com. SEOmoz was rebranded to Moz in 2013, and every page that was created before the rebranding has been redirected to a new URL.

A 302 Redirect, on the other hand, is known as “Found” or previously known as “Moved Temporarily”. It tells Google that the webpage needs to move to another URL temporarily.
For instance, For example, if you are faced with technical site difficulties, while you fix it, you want people who clicked on your URL to go to your temporary URL.
Link juice will not be passed from the old URL to the new URL.
Here’s how you can think of the 302 redirects:
You’re going for an internship overseas for 3 months. You then want to let your postal service to deliver your mails to your temporary home for that specific duration.
In the eyes of the average users, the redirect is the same as the 301 Redirect. The difference is this 302 redirect lets the search engine know that the website is just moving to another URL temporarily.
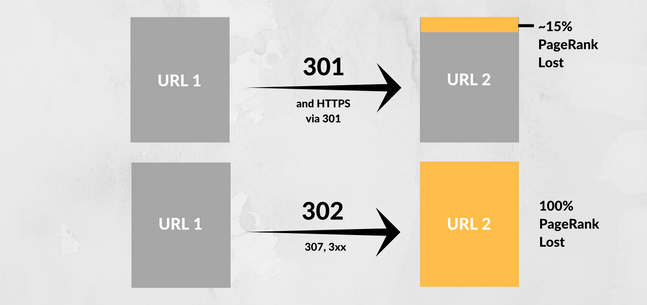
Did you know that using 301 URL forwarding would cost you a 15% Page Rank loss and a 302 URL forwarding costs a 100% Page Rank loss in the past?
You may have received advice to stay away from 302 redirects or even 301 too due to PageSpeed and indexing issue. But… if you don’t use redirects when you are removing/moving, your users will face a 404 broken page (also known as “Not Found”).
Google previously requested for webmasters to migrate their website from HTTP to HTTPS which requires webmasters to implement the 301s. As a result of the loss in page rank, webmasters neglected Google’s advice.
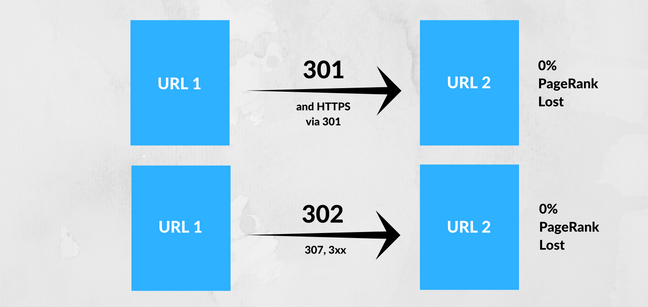
However, in 2016, Google’s engineer Gary Illyes shared that “30x redirects don’t lose PageRank anymore.”
30x redirects don’t lose PageRank anymore.
— Gary Illyes (@methode) July 26, 2016
Moz has created a test to confirm that the penalties have indeed been removed.
What’s best for SEO?
If you follow Gary’s advice and use the redirects the right way, you won’t have to face many indexing issues with Google.
Sometimes when content isn’t performing very well, we think to ourselves whether to delete them off the website. Tell me, what would you do? Would you keep the page or choose to remove it from your website?
Do you want to know what the right answer is? Here you go. You need to ask yourself a few questions as listed below:
When you want to remove a page, the first question to ask yourself is whether you have any pages that can substitute the page you want to delete. Do you have a page that provides similar content?
If you do, ask yourself if the content is coming back. If it is, create 302 redirect where it tells the search engine that the page is only temporarily unavailable. If it is not returning, create a 301 redirect. Delete your old page and redirect your visitors to the new webpage.
Imagine this, a visitor of yours stumbled across a link to another page of yours which has been deleted. Your visitor clicked on the link because you told him he could obtain more information by visiting another page of yours.
But as he clicked on it, he was shown a broken page, also known as, a 404 page. He gets disappointed and feels that your website isn’t updated. He decided to stop visiting your websites, forever!
We don’t want our visitors to stumble upon a broken page, ever…
You and I both know that user experience is Google’s number one priority. Therefore, it is a really good idea to add a 301 or 302 redirect whenever possible.
However, if you have no place to redirect the page to, consider sending a 410 HTTP header which is also known as “Gone”. It lets the search engine know that the URL won’t be back anymore and they can remove the URL from the index quicker compared to the 404 status code.
If you are using WordPress for your sites, you can take advantage of the simpler way of URL Forwarding which is using a plugin. Below are some of the plugins you may use:

Redirection is the most installed redirect manager for WordPress. It is completely free to use. Whether you have a few redirects or thousand of redirects, you may go for Redirection.
Besides URL forwarding, the plugin helps you to keep track of 404 errors as well. The reduced errors will help make your site better for your users.
SEO Redirection is another free WordPress plugin that helps you manage 301 redirects. Not just that, it manages 302 and 307 redirections as well as wild card redirection.

Last but not least, we have our plugin, SEOPressor Connect. URL Forwarding is one of the many features our plugin provides. All you need to do is type in the new link in the 301 Redirect URL box. It is as simple as that.
If you’re curious about what canonical URL is, it is a solution for duplicated contents. For example, you have to URL, let’s say “https://sugarjoe.com/candy-and-chocolate” and “https://sugarjoe.com/chocolate-and-candy”. Both of them shows the same content.
The search engine may not know which site it should send traffic to. Filling in the URL in the Canonical URL box clears things up for the search engine.
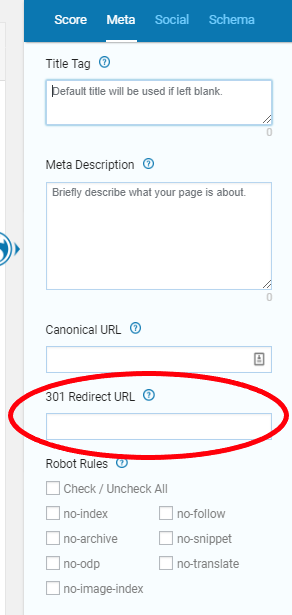
All you need to do is fill it in with your new URL
If you can choose whether or not to use a redirect, always choose not to use a redirect. Redirect slows down your page.
Imagine you are walking towards a restaurant recommended by a friend. When you’ve reached the doorstep, you saw a notice that they have moved a few blocks down the street.
It is the same as redirects. Redirects will result in a slower website because it takes time to go from one place to another.
Google recommends to minimize or if possible, completely eliminate the usage of redirects for optimal PageSpeed.
Using a redirect is handy when your page or content has been moved. It prevents your users from seeing a 404 error page which affects user experience.
Although a 301 and a 302 redirect is pretty similar to the eyes of an average user, you should always use redirects correctly. When you use the right redirects, you’re letting the search engine know what is going on on your site. Based on the redirects you’ve used, it lets the search engine know whether or not to pass down link juice.
As mentioned earlier, you should try to avoid using a redirect. Instead, spend some time to improve the content or webpage instead of deleting them.
Firstly, if you’re coming up with a new URL, you should take note of the URL structure. The URL structure does affect SEO. It is best to keep it short and relevant. There are many other things to consider as well when it comes to URL structure.
We’ve compiled it in an article and you can read them here: Does URL Structure Affect SEO? See What Google Thinks About Them
The second tip; if you need to delete a page, instead of showing a dull 404 page, you may design your own 404 page. Most websites inject humor on the 404 page to improve the user experience.
While you’re at it, don’t forget to add in a button where your visitors can click to return to your homepage. Having that button is beneficial. Instead of leaving your website after stumbling upon the page, users can view your homepage and also other pages you have.
Here is a list of beautifully designed 404 pages compiled by Search Engine Journal: 25 of the Best Examples of Beautifully Designed 404 Pages
Most of them are creative and cute! My favorite one is Number 5 by Emailcenter UK Ltd.
Let me know down below your favorite 404 page(s) on the list! Thank you for reading and I hope you learned a little more about redirects today. If you like this article, do share it around!
Updated: 13 July 2025

Save thousands of dollars (it’s 100x cheaper)

Zero risk of Google penalty (it’s Google-approved)

Boost your rankings (proven by case studies)
Rank High With This Link Strategy
Precise, Simplified, Fast Internal Linking.
