To better understand the value of co-citation for SEO, you first have to grasp what a backlink is and why it’s so crucial. Backlinks are inbound links to a website. Getting backlinks from high value sites that are relevant to your site is integral to SEO efforts.
You’ve probably heard of social signals, author rank, etc. (the trust signals that Google is trying to use to measure relevance), but you’ve probably never heard of co-citation, and it can be kind of hard to grasp, at first. And this is exactly why this course is here:
There are a total of 9 chapters, each targeting on different aspect of link building strategies.
Chapter 1: Building Links And Authority
Chapter 2: Guest Blogging And Relationship Management
Chapter 3: Link VS Social Popularity
Chapter 4: In-dept Article Series – The Powerful Internal Links
Chapter 5: Page Level And Link Relevancy
Chapter 6: Pitching The Media For Contribution, Get A Link From HuffingtonPost
Chapter 7: Link Baiting Legendary Content
Chapter 8: The New Era Of Link Building, What Works, What Does Not
Chapter 9: The Speed Of Attention, The Freshness Index
The chapters are also listed out on the side-bar for easy navigation.
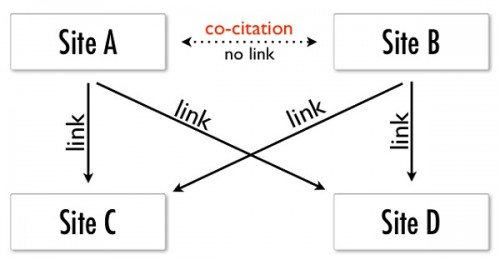
Co-citation for SEO means that the more often that your keywords appear near your company name on other websites of relevance, you’ll have a great chance of improving the search engine rankings for keywords that are specific to your industry.
Let’s look at co-citation from another angle. Sometimes, you have to read about it in a few different ways to really get a handle on it. Think back to when you were at college and when you were writing long essays. You had to write those difficult papers with lots of facts and reference all your sources in the essay. Even though you don’t have a link in the text, the search engines are getting so smart that they can see the volume and the correlation of high quality content related to it. Let’s look at the example of Consumer Reports.
You can look at a lot of the reports on the Internet that talk about reviews and cell phone and mention Consumer Reports. They don’t need to link to the page. In fact, very little of them ever link to this page. Several of them will do just this. If you see a text snippet on the page it might say, “Cell phones that are rated by Consumer Reports.”
That’s how co-citation was born. If there are hundreds of references on the Internet based around a specific topic from trusted writers who talk about the brand or company it could establish a very strong trust.
Basically, co-citation refers to one source talking about two different sources, thereby making a bridge between those two sources in a context. From a technical perspective, when we are talking about co-citation in the context of SEO, it’s not a really accurate label. A better label might Topic PageRank or Content Analysis.
Google is using all the data they have to more effectively analyze statistical correlations between websites to naturally affect and enhance search result sets.
The idea is that a social media post or website will link to your site, but it’s the kind of context in which the link happens that matters, not any unique keywords that are embedded into the link.
For example, if an article or website is talking about a topic inside your industry, and it refers to an article you wrote or your business, that’s considered a citation.
Just like anything in any industry, correlation does not necessarily mean causation. However, you have to not pay attention to the industry for a second and look in. What kind of user experience and brand credibility can you develop by doing this? You can do a whole lot! So, even if it doesn’t end up being a serious ranking factor, you have nothing else to lose! You are branding and marketing your company in a positive way by making high quality content that people really want to source and reference.