Steph W. from SEOPressor


...help you check your website and tell you exactly how to rank higher?
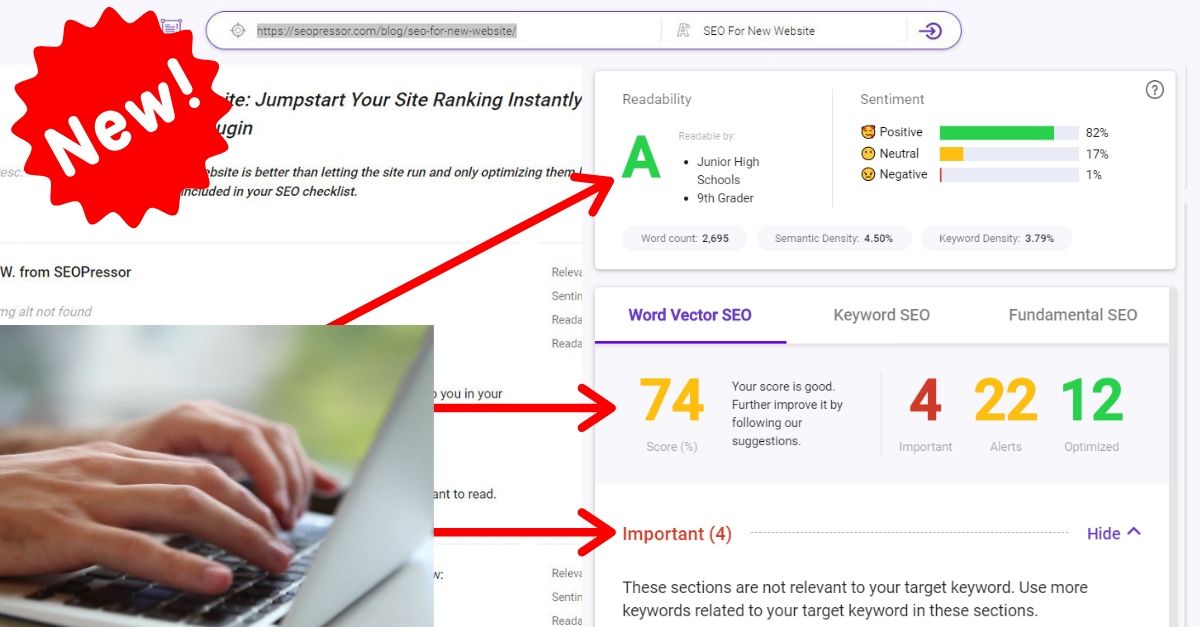

80
score %
SEO Score

Found us from search engine?
We rank high, you can too.
SEOPressor helps you to optimize your on-page SEO for higher & improved search ranking.
By winniewong on December 2, 2015

When talking about Google ranking factors, one thing that can be said for sure is that there’s an awful lot of speculations going on. From the total numbers of factors to what each of them are, you can find a lot of people with a lot different of opinions about them.
For example, the most popular myth about ranking factors is that there’s exactly 200 of them. Over the years people have been racing to identify what each of the 200 factors are, much like how people have been attempting to identify the 11 herb and spices of Colonel Sanders’ Secret Recipe.
The thing is, nobody (outside of Google of course) knows for sure how many ranking factors used by Google or what are they. The only amount ever stated by Google is that they are using over 200 factors and each of them can have more than 50 variations. That totals up to more than 10,000 factors!
Now, attempting to identify each of the 10,000 plus factors is definitely a wild goose chase. But the practical thing to do is to know enough of the confirmed ones so that your SEO efforts are in the right track. And the best way to do that in my opinion is by digging up Google’s own search engine patents.
You can read more on why patents are more reliable when it comes to sourcing SEO information in my previous post. For now, I’d like to discuss a very notable patent that might contain the key information on Google ranking factors.
In 2008 Google Inc. published a patent with the title “Information retrieval based on historical data”. The abstract of the patent states the following:
“A system identifies a document and obtains one or more types of history data associated with the document. The system may generate a score for the document based, at least in part, on the one or more types of history data.”
A document refers to any online assets that can be displayed as a search result on Google. In most cases this means websites and webpages. So what the patent is about is basically how Google ranks (scores) a website based on its history data (ranking factors).
The patent states that a website’s history data “may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document”. This means that these factors are used both to generate a ranking score for freshly indexed results as well as updating previous, already ranked results.
Another line states that Google “may generate (or alter) a score associated with a document based, at least in part, on information relating to the [history data] of the document”. What this means is each of the factors listed might affect a website’s ranking but not necessarily all of them are used at the same time. Google might use a combination of selected factors deemed necessary for a particular result or query.
Also, most of the factors listed includes a primary application as well as additional or alternative applications. This might be what Matt Cutts meant when he said “each of the factors may have variations”.
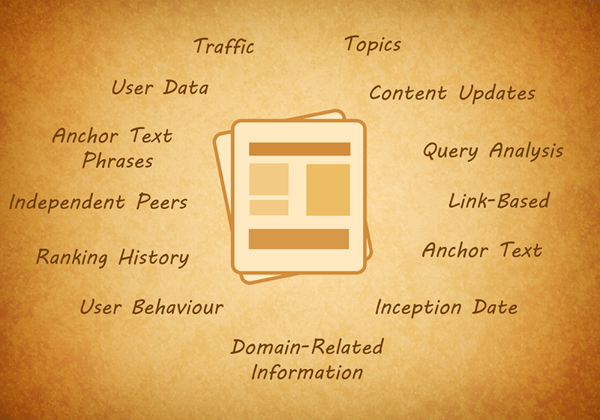
There are 13 examples of History Data listed in the patent. What I’ll do is to analyze each of the description to tell what they do in simpler words. Also I’ll note down the best practices that can be derived out of them:

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, a document’s inception date may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with that document.”
Inception date means that Google might use a website’s age to influence its ranking. There are few ways how Google determine inception date according to the patent:
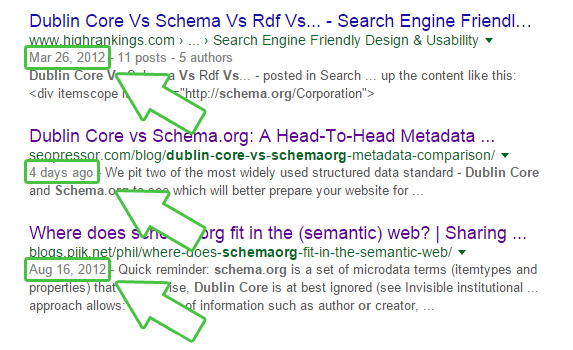
Google takes into consideration the age of a result when ranking them.
And here’s examples of how Google use a website’s inception age to affect its ranking:
This means that a newer website with less total backlinks can be ranked higher than an older website with more backlinks if the growth rate is higher.
This factor might bring either positive or negative scoring depending on the difference of age between the website and the other results.
There’s no one catch-all solution that can be derived from this particular factor but the general message is, website age matters. Here’s some of the key takeaways:

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information relating to a manner in which a document’s content changes over time may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with that document.”
This point describes a Content Update Score that can influence a website’s ranking. Content Updates/Changes deals with how a web contents changes overtime. A website that is ever-changing will be scored differently than websites that remains static.
The Content Update Score is made out of two components, each might take into account different factors:
The patent also states that Google might compare Content Update Score of a website from a period of time with another. This is so that a change trend can be plotted to see whether the trend is increasing or decreasing. The rate of increment or decrement will further influence the scoring.
Similar to Inception Date, Content Update Score can also be used to match different queries with different types of results based on their Content Update Score.
As a general rule, it’s important to keep your website updated. This factor also highlights the importance of content marketing as having new contents updated on a regular basis does in fact affect your ranking. So it’s highly recommended to add a blog or news section to your website on top of general information about your company or products.
Another point to consider is to update the whole look and feel of your website once in a while. On top of directly affecting your ranking, it also improves user experience that can indirectly improve your business overall.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, one or more query-based factors may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.”
Query-based factors takes into consideration the activity revolves around user queries. This factor basically discusses about the two-way relation between search results and user query.
Google will try to match the right query to the right results based on factors like the change of preferences in users when selecting the results for a particular query.
The factors can vary both on the results side as well as the query side. For example:
This factor mainly highlights the importance of keyword research. Before you even start creating contents to target, you have to first analyze the nature of queries or keywords you’re targeting, as well as your would-be competitors – the ones already ranking for those queries.
In targeting your keyword, take into consideration the following:

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, one or more link-based factors may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.”
Backlinks are pretty well-known factor when ranking websites even since the earliest days of Google. This patent reveals in more detail how links are used in factoring a website’s ranking, mostly revolving around link quality and growth rate. Some of the link-based factors are:
The link-based factors can be used by Google to achieve the following:
This factor tells us that while backlinks are important for ranking, Google takes into consideration more than just the total number of backlinks. Other factors such as Freshness and link quality let us know that not all links are scored the equally.
It is also important to keep track of your existing backlinks and take action when they disappear. Not much can be done for closed websites but you should look for those that replace linking to your content in favor for another presumably better contents.
You can try improving your replaced contents to be better than the one replacing it and request for the owner to link back to you.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information relating to a manner in which anchor text changes over time may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.“
Anchor text deals with the outbound link profile (in form of anchor text) of a website. A massive change in anchor text of a website might signal a change of direction or focus in the website so it can no longer be ranked according to its previous score.
When it comes to anchor text Google takes into account the following:
Most of this factor deals with the practice of purchasing older websites and abusing their ranking score. With this patent we know that it’s no longer valid since Google will reset the score once the anchor text profile changes.
Another thing to keep in mind is an anchor text that remains unchanged when a content is updated is a sign of its freshness. This is because the link it points out is still relevant despite the change of other elements of the content.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information relating to traffic associated with a document over time may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with the document.“
The amount of traffic a website get are also used by Google to influence its ranking. Some of the criteria used by Google when it comes to traffic:
Although the whole point of doing SEO is to get traffic in the first place, there are other methods of getting traffic you can do to kickstart some traffic to your contents. One example is by promoting your contents. Once traffic starts to come in, it will be used as a signal to improve your ranking and get even more traffic in return!
Another interesting point is that advertisements in your website can also impact the ranking. So rather than just displaying any random ads, be sure to display related, high quality ads so you can both earn from it as well as use them to improve your ranking at the same time.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information corresponding to individual or aggregate user behavior relating to a document over time may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with the document.“
User behaviour deals with how users interact with your website upon landing on them from the search results. Some of the metrics listed:
Presentation is important when it comes to getting users to interact with your website. For instance, even if you are ranked on the first page of Google it still doesn’t guarantee a lot of hits. In this case, your title, URL and snippet can be the difference between a click-through or scroll-through.
So try to view these components from a user’s perspective and see whether they are enough to satisfy the search intent. A good guideline is to replicate what the top-ranking results are doing with theirs.
Even when users click-through your results and end up at your contents, there are still a lot of things to be done to make them stay and keep on browsing.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information relating to a domain associated with a document may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with the document.”
Domain-related information takes into consideration the nature of how a website is hosted within a computer network. Factors that can affect a website’s ranking includes the following:
Most of the domain-related information are used to detect doorway domains or link farms used by black hat SEOs to manipulate search ranking. If you aren’t practicing these yourself you shouldn’t have much to worry.
But while Google is undoubtedly good at recognizing spammy domains and a legit one, it’s still a good idea to at least do some research on new domains you plan to acquire. If a domain have a history of being associated with shady websites such as pornography sites or obvious link farms then you might want to be extra careful.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information relating to prior rankings of a document may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with the document.”
Ranking history deals with the movement of a particular search result within the search result page. Things that are taken into consideration includes:
Google can use these factors for a number of purposes:
This factor let us know that even after our contents get ranked, you should still need to put efforts to maintain or improve it. Even if you ranked first, you might get overtaken by other results with better Ranking History.
If you notice a drop in the ranking of your contents then maybe it’s a good time to consider updating them to avoid them from being considered as outdated by Google.
You can also take advantage of viral topics by creating related contents to piggyback on the trend and get a boost of traffic by promoting them. By doing this Google will detect the correlation between the virality of your contents and the topic and rank you higher.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, user maintained or generated data may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.”
User maintained or generated data refers to information generated by users to indicate their interest in a website/webpage. User maintained or generated data can consists of the following:
How Google measure these signals are as the following:
The most straightforward way of taking advantage of user maintained/generated data is by simply providing valuable and actionable contents. If deemed important enough to be revisited time and time again, users will naturally add your contents to their bookmark and favorite lists.
Repeated visits will also generate more temporary files and cookies which will improve your ranking.
You can read my other article on other ways you can get users to return and stay longer on your site.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information regarding unique words, bigrams, and phrases in anchor text may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.“
The next on the list is quite a mouthful and unfortunately, is also a bit technical. But not to worry, I’ll be gentle. The concept is related to something known as web graph or link graph.
Web graphs maps the connection between websites/webpages through incoming and outgoing links between them. These links are usually associated with anchor texts that contains unique words, bigrams and phrases. As you might already know, anchor texts can tell a lot about the nature of links they are associated with.
Google may monitor a website’s web graph and their behaviour over time. And then they can use them for scoring, spam detection or other purposes.
Similar to other factors, this one is used to help determine the quality of links pointing to a website. By looking at the behaviour of web graphs, Google can tell whether links to a website are natural or spammy.
As long as you’re not getting links from unnatural methods you should do just fine. Moving along.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information regarding linkage of independent peers (e.g., unrelated documents) may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.”
Independent peers simply means unrelated websites. For example, Moz aren’t considered as an independent peer to say, Search Engine Land because both of them revolve around the same topic – SEO. McDonalds however, can be considered as independent peer to Moz since they are talking about two very different things.
So when a website receives a huge number of links from unrelated websites, it might signal a spamming attempt and Google will react accordingly.
Starting to sound like a broken record here – Don’t spam and you’ll do just fine.

“According to an implementation consistent with the principles of the invention, information regarding document topics may be used to generate (or alter) a score associated with a document.“
Pretty straightforward, Google might use the topics focused on a website to better match its ranking with related queries. Google extracts a website’s topic by these methods:
A website’s topics can be used in several manners:
What can be done is to have a clear focus of topics to be covered by your website and stick with it. If you need to cover a lot of topics especially if they are not closely related, consider instead to separate into multiple websites.
If you are considering to acquire new domains, it is also a good idea to find the ones closely related to your set of topics in order to benefit from the scoring previously associated with it.
So there you have it! While there’s a lot of practices can be derived from the ranking factors listed in this patent, it is important to note that not all of them needs to be executed all at once. Some might be suited for different situations and different types of contents and website.
So it’s very important to find the right combination that best suits you and your own website. Hope you find this post helpful and do ask if you need to get anything clear!
Updated: 9 February 2026

Save thousands of dollars (it’s 100x cheaper)

Zero risk of Google penalty (it’s Google-approved)

Boost your rankings (proven by case studies)
Rank High With This Link Strategy
Precise, Simplified, Fast Internal Linking.
