Steph W. from SEOPressor


...help you check your website and tell you exactly how to rank higher?
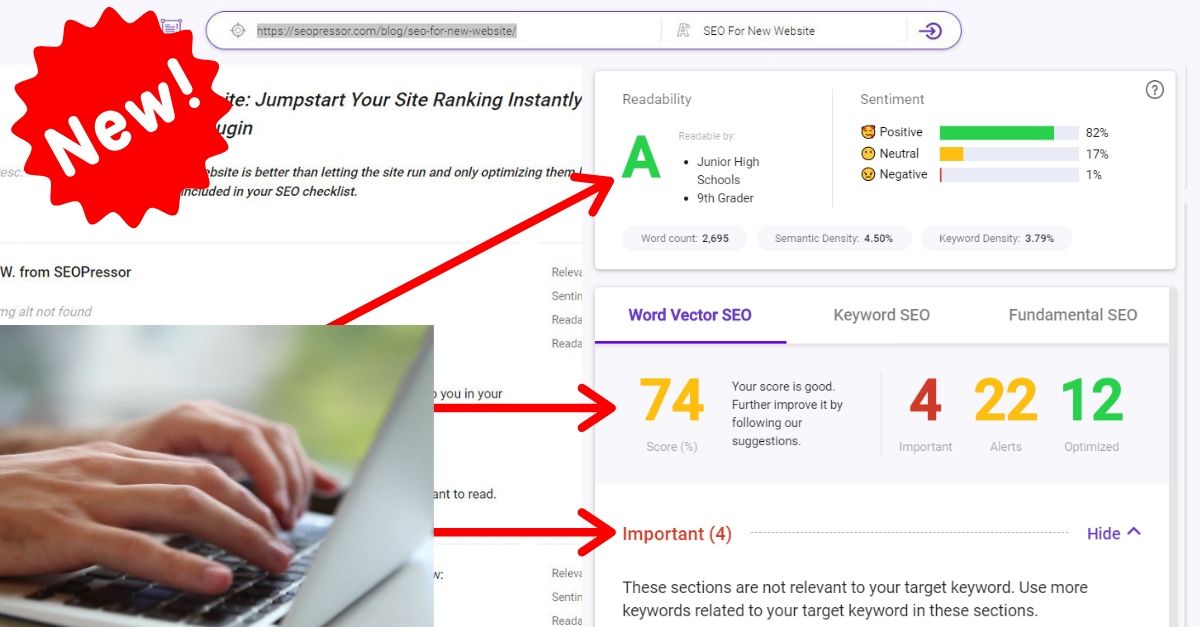

94
score %
SEO Score

Found us from search engine?
We rank high, you can too.
SEOPressor helps you to optimize your on-page SEO for higher & improved search ranking.
By jiathong on May 18, 2020

After hours of coding, writing, designing, and optimizing, finally you are ready to live your new web page. But hey, why is my blog post not showing on Google?
What have I done wrong?
Why does Google hate me?

Now, now, we have all been there and I have learned to give it at least a day or two before trying to search for my new blog post on Google.
Because I have long accepted that that’s how long Google needs to actually include newborns, I mean new blog post on Google Search. Sometimes it takes even longer for new websites.
While the process of getting a new page or website on Google Search is a long and windy one, but it’s one worth learning about.
Let’s start with the basics.
[bof_display_offer id=29944]
There’s no one to better explain this than Google themselves. So here’s a video from Google with Matt Cutts explaining about how search works.
Have you watched it? If yes, let’s recap and summarize.
For content to show up on Google Search, it has to go through spiders. No, not real spiders, but a program called spider.
The spider will start with a link, which it will then crawl through the content. If they see another link embedded in the content, they will crawl it too, and the process repeats.
Crawled contents, or web pages, are then stored in Google’s index. When a user made a query, answers are pulled from the index.
So in order for your content to show on Google Search, you have to first make sure your website is crawlable by Google’s crawler called Googlebot.
Then you have to make sure it’s indexed correctly by the indexer which is called Caffeine. Then only will you see your content or website appearing on Google Search.
Here’s the thing, how do you check from Google for exactly whether or not they have indexed your content? Well, you can’t. Like all things in SEO, the next best strategy you can do is analyze and give it your best guess.
Try typing into the Google search bar site:insertyourdomainhere.com and enter, Google Search will give you a list of all indexed web pages from your domain. Or better yet, search your URL directly on Google.
But, as Matt Cutts said, web pages that are not crawled CAN appear on Google Search as well. Well, that’s another topic for another day.
Still interested? The video is only 4 minutes long. Do take a look to understand more.
Anyways, let’s get back to the topic. So when do you start asking:
For me, I will give it at least a couple of days, at most a week, until I start freaking out on why my content is still not appearing on Google Search.
If it has been more than a week, or even a month and your website is still not there.
Here is a list you need to start checking to see what is stopping Google from indexing your content or website:
Sometimes a little-overlooked detail can have a big effect.
Robots.txt is the first place that Googlebot visits on a website in order to know which web pages are nofollow or no-index and such.
Do you have this in your HTML head section?
![]()
The robots noindex tag is handy to make sure that a certain page will not be indexed, therefore not listed on Google Search.
Commonly used when a page is still under construction, the tag should be removed when the web page is ready to go live.
However, because of its page-specific nature, it comes as no surprise that the tag may be removed in one page, but not another. With the tag still applies, your page will not be indexed, therefore not appearing in the search result.
Similarly, an X-Robots-Tag HTTP header can be programmed into the HTTP response. This can then be used as a site-wide specific alternative for the robots meta tag.
![]()
Again, with the tag applied, your page will not show up in Search. Make sure to fix them.
Read more about meta tags here: How To Control Web Crawlers With Robots.txt, Meta Robot Tags & SEOPressor
Googlebot is generally a patient bot, they would go through every link they can come across and do their best to read the HTML then pass it to caffeine for indexing.
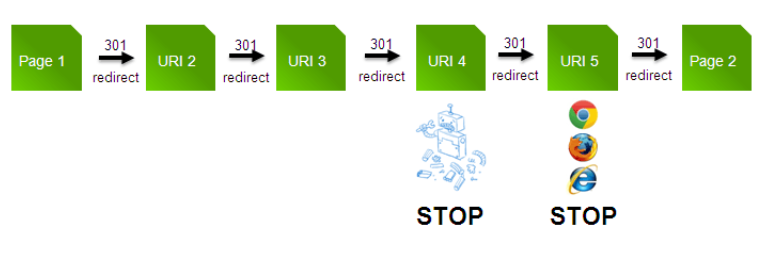
However, if you set up a long winding redirection, or the page is just unreachable, Googlebot would stop looking. They will literally stop crawling thus sabotaging any chance of your page being indexed.
Not being indexed means not being listed on Google Search.
I’m perfectly aware that 30x is useful and crucial to be implemented. However, when implemented incorrectly, that can ruin not only your SEO but also the user experience.
Another thing is to not mix 301 and 302. Is it moved permanently or moved temporarily? A confused Googlebot is not an efficient Googlebot.
Hear it from Google themselves.
So make sure that all of your pages are healthy and reachable. Fix any inefficient redirect chains to make sure they are accessible by both crawlers and users alike.
A canonical tag is used in the HTML header to tell Googlebot which is the preferred and canonical page in the case of duplicated content.
For example, you have a page that is translated into German. In that case, you’d want to canonical the page back to your default English version.
![]()
Every page should, by advise, have a canonical tag.
Either to link it back to itself in the case where it is a unique content. Or link it to the preferred page if it is duplicated.
Here comes the question, is the link you canonical to correct?
In the case of a canonical page and its duplicates, only the canonical page will appear on Google Search. Google uses the canonical tag as an output filter for search.
Meaning, the canonical version will be given priority in the ranking.
If that is not your purpose, fix your canonical and link it back to itself. That would do the trick.
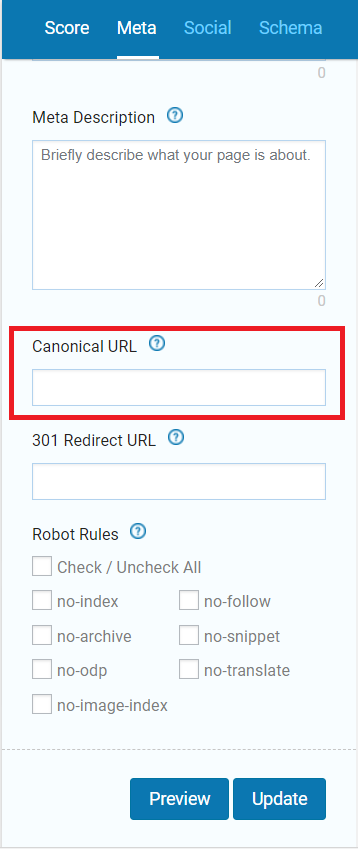
SEOPressor Connect let you skip the step of manually inputting the canonical tag.
Google has thousands of machines to run spiders, but there are a million more websites out there waiting to be crawled.
Therefore, every spider arrives at your website with a budget, with a limit of how many resources they can spend on you. This is the crawl budget.

I’m on a budget.
Here’s the thing, as mentioned before, if your websites have a lot of redirection chains, that will be unnecessarily eating your crawl budget. Note that our crawl budget might be gone before the crawler even reaches your new page.
How to know how much is your crawl budget? In your Search Console account, there will be a crawl section where you can check your crawl stats.
Let’s say your website has 500 pages, and Googlebot is only crawling 10 pages on your site per day. That crawl budget will not be efficient enough for the new pages that you’re pumping out.
In that case, there are a few ways to optimize your crawl budget.
First of all, authoritative sites tend to be given a bigger and more frequent crawl budget. So get those backlinks. The more quality and relevant links pointing to your website mean your website IS of good quality and high relevance to your niche.
We all know building up authority doesn’t happen in one day. So another thing that you can do is to make sure that your site can be crawled efficiently.
You need to make good use of your robots.txt file. We all have some pages on our website that don’t really need to be up there in Search like duplicate content, under construction pages, dynamic URLs, etc.
You can specify which crawler the instruction applies and which URL strings should not be crawled. As an example:
![]()
That way, crawlers won’t be spending unnecessarily budget on pages that don’t need crawling.
A list of the most common user agents includes:
One important thing that I have already mentioned above that also applies in optimizing your crawl budget is to fix those redirect chain. They are not only inefficient they are also eating up your crawl budget.
If they are any pages returning with a 40x errors, fix those too.
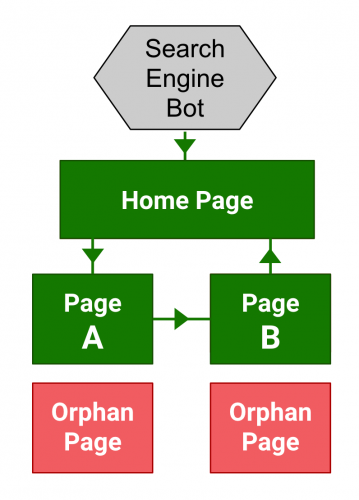
An orphan page is a page that has no internal links. Perhaps the link is faulty causing the page to be unreachable, or during a website migration, the link is accidentally removed.
Remember how the spiders work? They start from one URL and from there they crawl to other URLs that are linked.
An orphan page can’t be crawled because there is no way to be crawled. It is not linked from your website, thus the term orphan. That’s why interlinking is so important because it acts as a bridge for the crawlers from one page of your content to another.
Read more about interlinking here: Why Internal Links Matter To Your SEO Effort?
How can you identify orphan pages?
If you’re like us and you’re using the WordPress CMS you can export a full list of URLs of every pages and content on your website. Use that to compare with the unique URLs found in a site crawl.
Or you can look up your server’s log file for the list of unique URLs loaded for let’s say the last 3 months. Again, compare that with the list you got from the site crawl.
To make your life easier, you can load those data into an excel file and compare them. The URLs which are not duplicated are the ones that are orphaned.
After knowing what are the orphaned pages, fixing them would be much easier.
Now what you need to do is link those orphan pages appropriately. Make it so they are easily discoverable by users and crawlers alike. Also, don’t forget to update your XML sitemap.
If everything is working nicely, there are no error codes returning, the robots tags are fine, but your page is still not showing up. Why?
Well, the issue might very well be from Google’s side.
Maybe you are just not the crawler’s priority.

Spidey, don’t be sleeping on the job now.
[bof_display_offer id=29944]
Google only has so many resources. And the bigger and more authoritative websites will be allocated a bigger and more frequent crawl budget. So, how can you change that?
Submitting your sitemap to Google is like telling them “Hey, here! Check out these important URLs from my website and crawl them!”
They might not start crawling those URLs immediately but at least you gave them a heads-up.
If you run a huge site that updates constantly, keeping up with your robots and multiple sitemaps will probably drive you nuts.
Do it in moderation and keep in mind that you can’t have no-index, nofollow on your robots and then add them to your sitemap. Because do you want it indexed or not?
To avoid things like to happen, maintaining a dynamic ASPX sitemap will probably be your best choice.
Update: Submit URL to Google search engine is no longer working because Google retired its public URL submission tool.
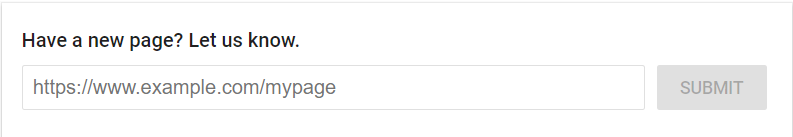
Similarly, Google lets you manually submit your new page to them.
It’s really simple. Just search for submit URL to Google and the search result will return you with an input bar. Now, copy and paste the URL of your new page and click on the submit button.
Voila, you have done submitting a new URL to Google for crawling and indexing.
However, just like the sitemap, this only acts as a heads-up for Google to make them aware of the existence of your new page.
Just do it anyways when your web page has been sitting there for a month and still not being indexed. Doing something is better than nothing right?
You can request, directly to Google, for a re-crawl and re-index of your page.
That can be done by logging into your Search Console then perform a fetch request via fetch as Google.
After making sure that the fetched page appears correctly: all the pictures are loaded, there are no broken scripts, etc. You can request for indexing, then choose between the option of crawling only this single URL or any other URLs that are directly linked.
Again, Google warned that the request will not be granted immediately. It can still take up to days or a week for the request to be completed.
But hey, taking an initiative is better than sit and wait right?
Once again, domain authority affects how frequent and how much your crawl budget will be.
If you want your new pages and website changes to be indexed swiftly, you have a better chance if your page rank is high enough.
High domain authority sites like Reuters gets index faster
This is a matter of slow and steady win the race though. If you can get a million backlinks based on one single content in a single day, that’s great.
But one great content is not enough. Your website needs to be updated frequently and consistently with quality content while simultaneously gain quality backlinks for your page authority to go up.
Start updating your website at least twice weekly, reach out to the community to build brand awareness and connections.
Keep that effort up, slowly and steadily your authority will go up and your website will be crawled and indexed much faster.
Here are some extra tips to increase your DA.
Here’s the thing, when you have a website that loads fast, Googlebot can, therefore, crawl it faster.

In the unfortunate case where the load speed of your website is not satisfying and requests frequently time out, you’re really just wasting your crawl budget.
If the problem stems from your hosting service you should probably change to a better one. On the other hand, if the problem comes from your website structure itself, you might need to consider cleaning up some codes. Or better yet, make sure it is well optimized.
Read more about page speed and SEO here: The Connection Between Site Speed and SEO Today
One thing that people always tend to forget is that your web pages are not a done and forget about it kind of deal.
You need to keep monitoring it to make sure that it’s not breaking, and of course, you also want to make sure that it’s ranking and bringing in the crowd that you need for marketing leads or potential clients.
A tool that we can recommend here in SEOPressor to help your rank tracking needs is BiQ Cloud’s Rank Tracking module.
![]()
This is a handy tool that will track your ranking pages daily, so you can keep an eye on your day to day ranking. I’d argue that this is an important stats to keep an eye on. Because if your ranking is dropping then it means
1) something broke,
2) your competitors are getting better.
Knowing what is happening to your website is an essential step in getting the ranks and traffic that you want.
So do not ever forget to keep track of your rankings.
Now, have you gotten a clear idea on why your website and URL is not on Google search? Here’s a quick checklist.
Updated: 17 July 2025

Save thousands of dollars (it’s 100x cheaper)

Zero risk of Google penalty (it’s Google-approved)

Boost your rankings (proven by case studies)
Rank High With This Link Strategy
Precise, Simplified, Fast Internal Linking.
